Transformers are an essential component of electrical power systems, responsible for stepping up or stepping down voltage levels to ensure efficient transmission and distribution of electricity. When it comes to rating transformers, the unit used is kilovolt-amperes (KVA). But why are transformers rated in KVA? Let’s explore the reasons behind this industry standard.
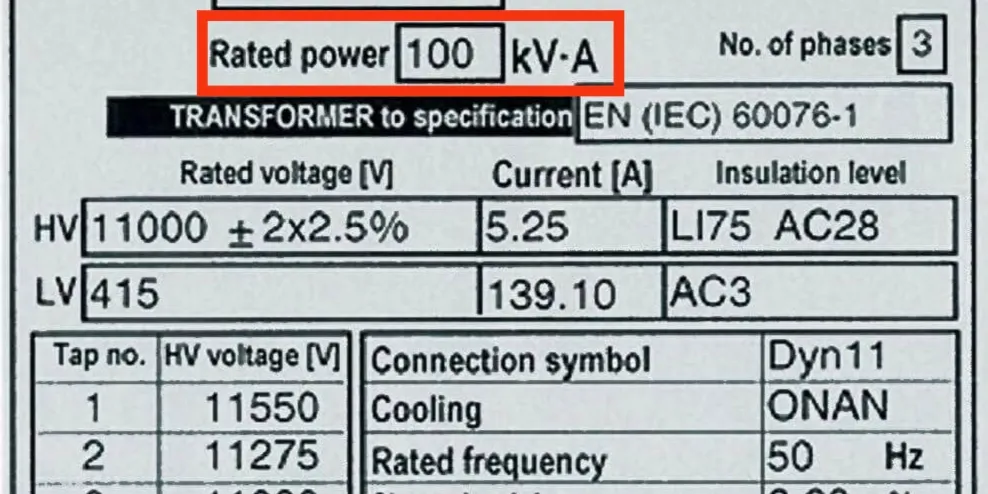
Table of Contents
What is KVA?
KVA stands for kilovolt-amperes, which is a unit used to measure the apparent power in an electrical circuit. It takes into account both the voltage and the current in the circuit, without considering the power factor. KVA represents the total power capacity of a transformer, including both the active power (measured in kilowatts, or KW) and the reactive power (measured in kilovolt-amperes reactive, or KVAR).
Why not use KW?
While kilowatts (KW) represent the actual power consumed or delivered by a transformer, it does not account for the reactive power component. Reactive power is necessary for the magnetization of the transformer’s core and the establishment of the magnetic field. Neglecting the reactive power can lead to inaccurate sizing and inefficient operation of the transformer.
Importance of Reactive Power
Reactive power is crucial for maintaining voltage stability and ensuring the proper functioning of electrical equipment. It compensates for the phase difference between voltage and current in an alternating current (AC) circuit. By including the reactive power in the rating, transformers can handle the reactive loads and maintain a stable voltage level.
Accounting for Power Factor
The power factor is a measure of how effectively electrical power is being used in a circuit. It is the ratio of real power (KW) to apparent power (KVA). Transformers rated in KVA allow for the consideration of power factor when determining the actual power capacity of the transformer. This ensures that the transformer can handle the real power demands of the connected load while accounting for any reactive power requirements.
Standardization and Compatibility
Using KVA as the rating unit for transformers allows for standardization and compatibility across the industry. It ensures that transformers from different manufacturers can be easily compared and selected based on their power capacity. Additionally, it simplifies the design and specification process for electrical systems, making it easier to determine the appropriate transformer size for a given application.
Conclusion
Transformers are rated in KVA to account for both the active power and the reactive power requirements of electrical systems. By using KVA as the rating unit, transformers can handle the total power demands of the connected load, maintain voltage stability, and ensure efficient operation. This industry standard allows for standardization, compatibility, and accurate sizing of transformers, making it easier for professionals to design and specify electrical systems.
Reference: Transformer – Wikipedia, Volt-ampere – Wikipedia



