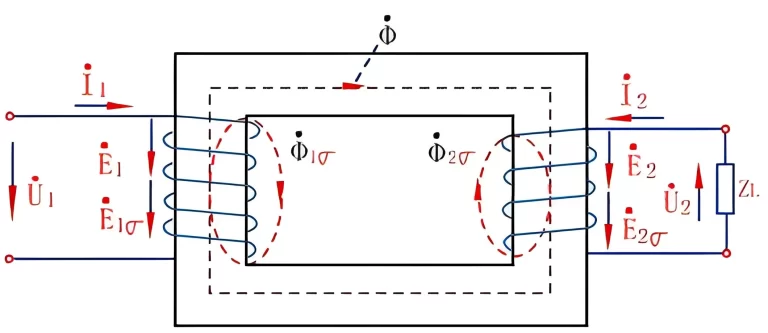
Transformer oil plays a critical role in the performance and longevity of electrical transformers. It serves as both an electrical insulator and a coolant, ensuring that the transformer operates efficiently and safely. However, over time, transformer oil can degrade and become contaminated, potentially leading to equipment failure and costly repairs. That’s why regular testing of transformer oil is essential to maintain the health and reliability of the transformer.

Table of Contents
Why is testing transformer oil important?
Transformer oil testing is a proactive approach to identify potential issues before they escalate into major problems. By analyzing the oil’s properties and detecting any contaminants or degradation, technicians can assess the condition of the transformer and take appropriate actions to prevent failures. Regular testing helps in:
- Identifying early signs of insulation breakdown
- Detecting moisture content and preventing corrosion
- Monitoring the presence of dissolved gases
- Assessing the oil’s dielectric strength
- Evaluating the overall condition of the transformer
How often should transformer oil be tested?
The frequency of transformer oil testing depends on various factors, including the transformer’s age, operating conditions, and criticality. However, industry standards recommend testing transformer oil at least once a year. This annual testing provides a baseline for comparison and helps track any changes in the oil’s properties over time.
In addition to the annual tests, certain situations may warrant more frequent testing. For example, if the transformer operates in a harsh environment with high humidity or extreme temperatures, more frequent testing may be necessary to monitor the oil’s condition closely.
Furthermore, if the transformer has a history of issues or has undergone repairs or modifications, it is advisable to conduct additional tests to ensure that the corrective measures have been effective.
What tests are performed on transformer oil?
Transformer oil testing involves a series of laboratory tests to evaluate the oil’s physical and chemical properties. Some of the common tests include:
- Dielectric breakdown voltage test
- Moisture content analysis
- Dissolved gas analysis
- Acidity test
- Interfacial tension test
- Power factor test
These tests provide valuable insights into the condition of the transformer and help determine if any corrective actions are necessary.
In conclusion
Regular testing of transformer oil is crucial to ensure the reliable and safe operation of electrical transformers. By adhering to industry standards and conducting annual tests, potential issues can be identified early, allowing for timely maintenance and preventing costly failures. Remember, prevention is always better than cure when it comes to transformer health!
References:
Transformer oil – Wikipedia
Transformer oil testing – Wikipedia