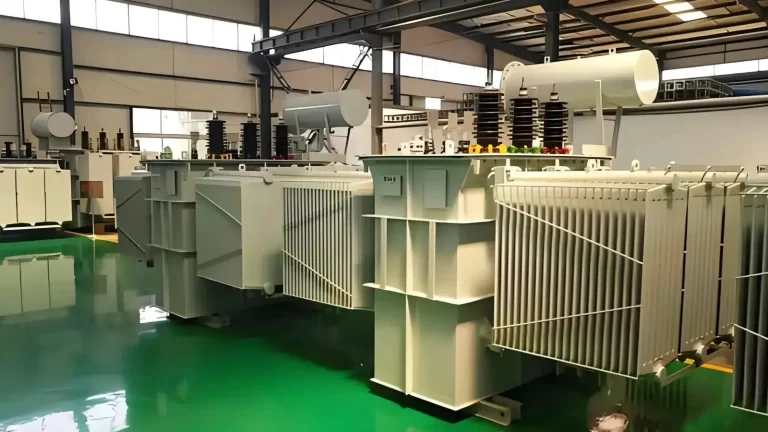
A power transformer is a crucial component in a substation that plays a vital role in the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. It is a static device that transfers electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. The primary purpose of a power transformer is to step up or step down the voltage levels to facilitate efficient power transmission.

Table of Contents
How does a power transformer work?
A power transformer consists of two or more windings, known as primary and secondary windings, which are wound around a common magnetic core. The primary winding is connected to the high-voltage side, while the secondary winding is connected to the low-voltage side. The windings are insulated from each other to prevent electrical leakage.
When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field in the core. This magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding through electromagnetic induction. The voltage induced in the secondary winding depends on the turns ratio between the primary and secondary windings.
What are the key components of a power transformer?
A power transformer consists of several key components that work together to ensure efficient and reliable power transmission:
1. Core: The core is typically made of laminated sheets of high-grade electrical steel. It provides a low reluctance path for the magnetic flux and reduces energy losses.
2. Windings: The windings are made of copper or aluminum conductors and are insulated to prevent electrical short circuits. The number of turns in the windings determines the voltage ratio between the primary and secondary sides.
3. Insulation: Insulation materials such as paper, oil, or synthetic materials are used to insulate the windings and prevent electrical breakdown.
4. Tap Changer: A tap changer is a device that allows the adjustment of the transformer’s output voltage to compensate for variations in the input voltage or load conditions.
5. Cooling System: Power transformers generate heat during operation. Cooling systems, such as oil or air cooling, are employed to dissipate this heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures.
Why are power transformers important in substations?
Power transformers are essential in substations for several reasons:
1. Voltage Regulation: Power transformers enable voltage levels to be stepped up or stepped down, ensuring efficient transmission and distribution of electrical energy over long distances.
2. Power Transfer: Power transformers facilitate the transfer of electrical power from the generation source to the distribution network, ensuring reliable and uninterrupted power supply.
3. Fault Isolation: Power transformers help isolate faults in the electrical system, preventing them from spreading to other parts of the network and minimizing the impact of disruptions.
4. Load Balancing: By adjusting the tap changer, power transformers can balance the load between different circuits, ensuring optimal utilization of the electrical infrastructure.
5. Voltage Conversion: Power transformers allow for the conversion of electrical energy between different voltage levels, enabling compatibility between different parts of the power grid.
In conclusion, power transformers are critical components in substations that enable efficient power transmission and distribution. Their ability to step up or step down voltage levels, along with other key functionalities, ensures reliable and uninterrupted power supply to consumers.
Reference:
Substation Transformers