Transformers are essential components in electrical systems, responsible for transferring electrical energy between circuits. They are used in various applications, including power distribution, voltage regulation, and electrical isolation. But have you ever wondered how many parts make up a transformer? In this blog post, we will explore the different components that come together to create this vital electrical device.
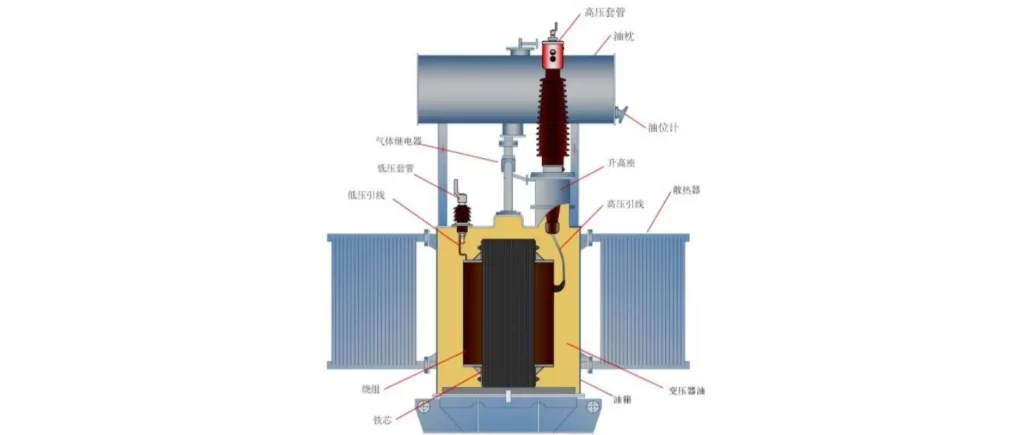
Table of Contents
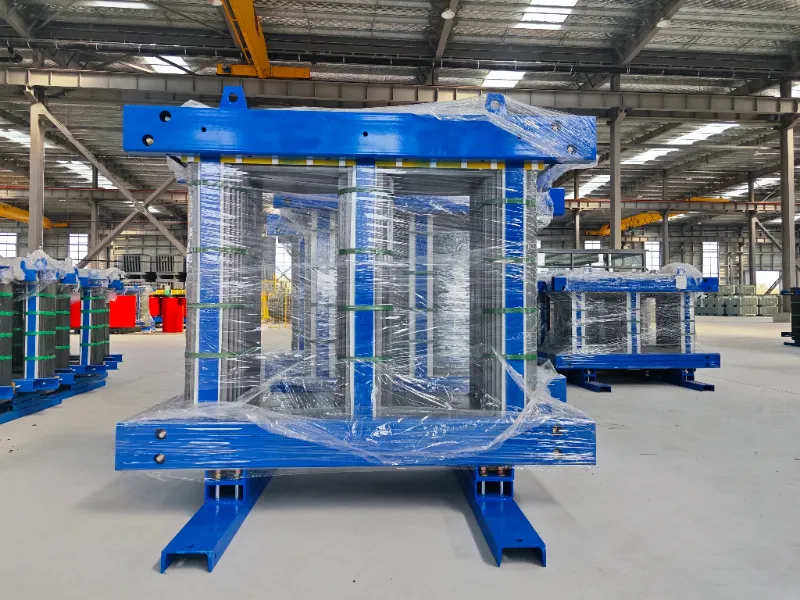
1. Core
The core is the central part of a transformer and is typically made of laminated steel. Its primary function is to provide a path for the magnetic flux generated by the primary winding. The core’s design and material play a crucial role in determining the transformer’s efficiency and performance.

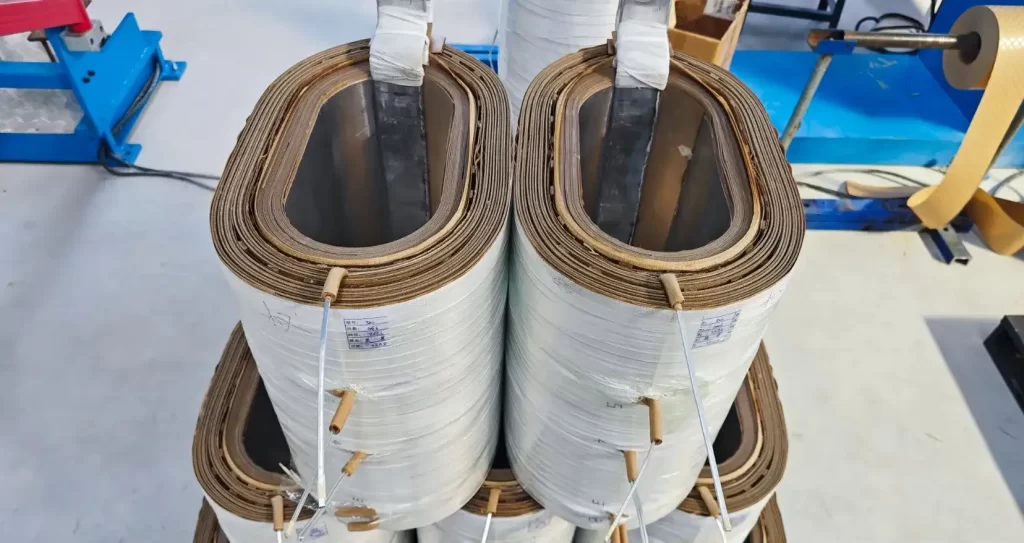
2. Windings
Transformers have two sets of windings: the primary winding and the secondary winding. The primary winding is connected to the input voltage source, while the secondary winding is connected to the load. These windings consist of insulated copper or aluminum wires wound around the core. The number of turns in each winding determines the voltage ratio between the primary and secondary sides.

3. Insulation
Insulation is a critical component in transformers as it prevents electrical leakage and ensures the safety and reliability of the device. Insulating materials such as paper, varnish, and enamel are used to separate the windings and provide insulation between different parts of the transformer.

4. Tap Changer
A tap changer is an optional component found in some transformers. It allows for the adjustment of the transformer’s output voltage to compensate for variations in the input voltage or load conditions. Tap changers can be either manual or automatic, depending on the application and requirements.
5. Cooling System
Transformers generate heat during operation, and a cooling system is necessary to maintain optimal operating temperatures. Cooling methods can vary, including natural convection, forced air, oil immersion, or liquid cooling. The choice of cooling system depends on factors such as transformer size, application, and environmental conditions.
6. Tank and Accessories
A transformer is housed in a tank, which provides mechanical support and protection to the internal components. The tank is typically made of steel and is designed to withstand various environmental conditions. Additionally, transformers may have accessories such as bushings, conservator tanks, and monitoring devices to enhance their functionality and performance.
These are the primary components that make up a transformer. Each component plays a crucial role in ensuring the efficient and reliable transfer of electrical energy. Understanding the different parts of a transformer can help in troubleshooting and maintaining these devices, ensuring their longevity and optimal performance.
Next time you see a transformer, you’ll have a better understanding of the intricate components that work together to power our electrical systems.
References:
Transformer Theory and Application
Transformer – Wikipedia