Transformers are essential devices in the field of electrical engineering. They play a crucial role in transferring electrical energy from one circuit to another. But have you ever wondered if the power changes during this process? Let’s dive into the world of transformers and explore the concept of power transformation.
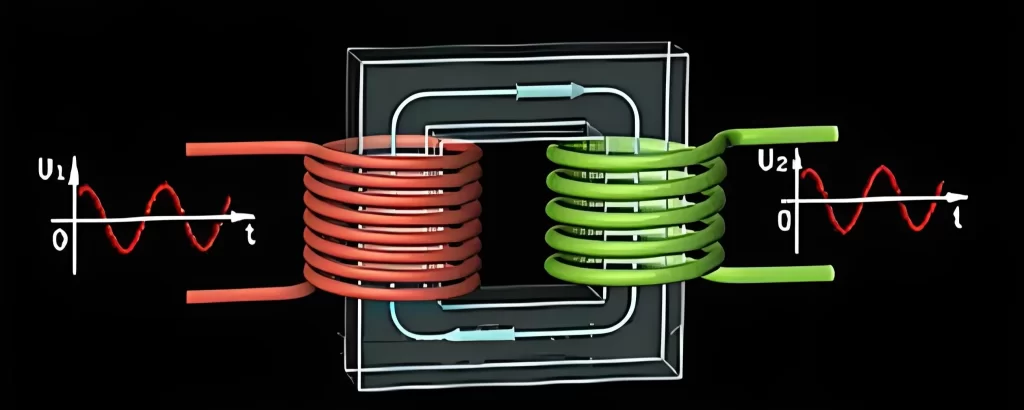
Table of Contents
What is a Transformer?
A transformer is an electrical device that consists of two or more coils of wire, known as windings. These windings are electrically insulated and wound around a core made of magnetic material. The primary winding is connected to the input voltage source, while the secondary winding is connected to the load.
How Does a Transformer Work?
Transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When an alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a changing magnetic field in the core. This changing magnetic field induces a voltage in the secondary winding, which is then used to power the load.
Does Power Change in a Transformer?
No, the power does not change in a transformer. According to the law of conservation of energy, power remains constant in an isolated system. In an ideal transformer (one without any losses), the power input to the primary winding is equal to the power output from the secondary winding.
Understanding Power in a Transformer
To understand power in a transformer, we need to consider two important factors: voltage and current. The power (P) in an electrical circuit can be calculated using the formula:
P = V x I
Where P is power, V is voltage, and I is current.
Primary and Secondary Power
In a transformer, the primary winding has a certain voltage (V1) and current (I1), while the secondary winding has a different voltage (V2) and current (I2). The power input to the primary winding (P1) can be calculated as:
P1 = V1 x I1
Similarly, the power output from the secondary winding (P2) can be calculated as:
P2 = V2 x I2
Power Transformation in a Transformer
Although the power input and output are different in terms of voltage and current, the product of voltage and current (V x I) remains the same in an ideal transformer. This means that the power input is equal to the power output:
P1 = P2
Efficiency and Power Loss
In real-world transformers, there are certain losses that result in a decrease in power output compared to the power input. These losses include resistive losses in the windings, core losses, and stray losses. The efficiency of a transformer is defined as the ratio of output power to input power and is given by:
Efficiency = (P2 / P1) x 100%
In Conclusion
Power does not change in a transformer. The power input to the primary winding is equal to the power output from the secondary winding, according to the law of conservation of energy. However, real-world transformers experience losses, which affect the efficiency of the device. Understanding power transformation in transformers is crucial for electrical engineers and anyone interested in the field of electrical energy.
Reference:
Does power stay the same in transformers? – Energy Education



