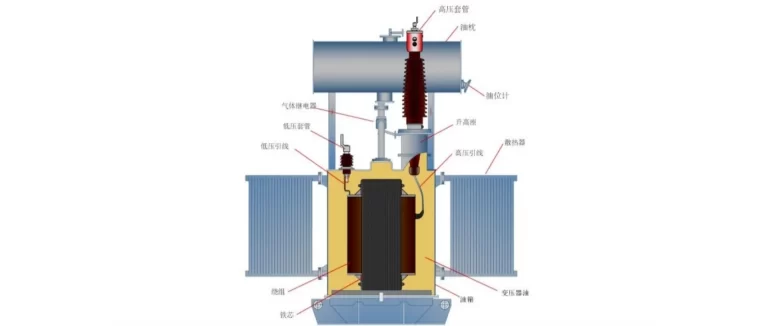
Transformers are essential components in many electronic devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and power adapters. These devices rely on transformers to convert electrical energy from one voltage level to another. However, a common concern among users is whether transformers continue to consume power even when not in use. In this blog post, we will explore this question and provide you with the facts.
Table of Contents
Understanding Transformers
Before delving into the power consumption of transformers, it’s important to understand how they work. Transformers consist of two coils of wire, known as the primary and secondary windings, which are wound around a magnetic core. When an alternating current (AC) passes through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding.
Power Consumption in Transformers
When a transformer is actively converting electrical energy, it does consume power. However, the power consumption of a transformer when not in use is negligible. Transformers are designed to be highly efficient, with minimal power losses. The majority of power losses occur during the conversion process, when the transformer is actively transferring energy from the primary to the secondary winding.
When a device is turned off or not in use, the transformer is essentially idle. It is not actively converting energy, and therefore, its power consumption is extremely low. In fact, the power consumed by a transformer in standby mode is typically less than 0.5% of its rated power.
Standby Power Consumption
While transformers themselves have minimal power consumption when not in use, it’s important to note that some electronic devices may still consume power in standby mode. Standby power refers to the energy consumed by a device when it is turned off but still plugged into a power source.
Standby power consumption is primarily attributed to other components within the device, such as standby power supplies and control circuits. These components may draw a small amount of power to maintain certain functions, such as remote control functionality or instant-on features.
Reducing Standby Power Consumption
To minimize standby power consumption and reduce energy waste, manufacturers have implemented various measures. One common approach is the use of power-saving features, such as automatic power-off or sleep modes. These features allow the device to enter a low-power state when not in use, reducing overall power consumption.
Additionally, energy-efficient standards and regulations have been established to encourage manufacturers to design devices with lower standby power consumption. These standards aim to promote the development of energy-saving technologies and raise awareness among consumers about the importance of reducing standby power.
The Bottom Line
In conclusion, transformers themselves have minimal power consumption when not in use. The power consumed by a transformer in standby mode is negligible, typically less than 0.5% of its rated power. However, it’s important to be aware that standby power consumption may still exist in electronic devices due to other components. To minimize energy waste, it is recommended to utilize power-saving features and choose devices that comply with energy-efficient standards.
Reference:
Transformer idle consumption