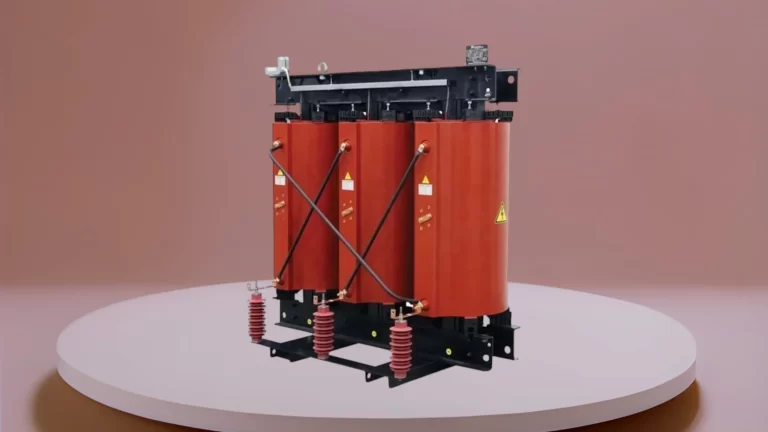
Dry-type transformers and oil-type transformers differ primarily in their cooling and insulation methods. Here are the key differences between the two:
- Cooling Medium:
- Dry-Type Transformer: Uses air or other gases for cooling. Ventilation and convection are the primary cooling mechanisms.
- Oil-Type Transformer: Immersed in insulating oil, which serves both as a cooling medium and an insulator.
- Cooling Mechanism:
- Dry-Type Transformer: Relies on natural air circulation or forced-air fans for cooling. Some may use additional features like heat sinks or ducts to enhance cooling efficiency.
- Oil-Type Transformer: Uses the heat dissipation properties of the insulating oil to cool the transformer. In larger transformers, additional cooling systems such as radiators or oil pumps may be employed.
- Environment and Safety:
- Dry-Type Transformer: Considered more environmentally friendly and safer due to the absence of flammable liquids like oil. They are often used in indoor installations or in areas with strict safety and environmental regulations.
- Oil-Type Transformer: The presence of oil raises concerns about environmental impact and fire safety. Spillage or leaks of oil can be hazardous, and additional measures may be required for containment and mitigation.
- Maintenance:
- Dry-Type Transformer: Generally requires less maintenance compared to oil-filled transformers. There is no need for oil testing, filtering, or periodic replacement.
- Oil-Type Transformer: Requires regular monitoring of oil quality, periodic oil testing, and, in some cases, filtration or oil replacement. Maintenance can be more involved.
- Applications:
- Dry-Type Transformer: Commonly used in indoor installations, buildings, data centers, hospitals, and areas where environmental and safety concerns are critical. They are also suitable for locations where space is limited.
- Oil-Type Transformer: Often used in outdoor installations, power substations, and industrial settings. Larger power transformers, especially those with high power ratings, are typically oil-filled.
- Cost:
- Dry-Type Transformer: Generally has a higher upfront cost but may have lower overall life cycle costs due to reduced maintenance requirements.
- Oil-Type Transformer: May have a lower initial cost, but ongoing maintenance costs, including oil testing and handling, can add up over time.
Ultimately, the choice between dry-type and oil-type transformers depends on various factors, including the application requirements, safety considerations, environmental regulations, and available space. Each type has its advantages and limitations, and the selection is based on the specific needs of the electrical system and the preferences of the end user.